Java: Classes
Introduction
A class defines the abstract characteristics of a thing (object), including its attributes and what it can do. Every Java program is composed of at least one class.
From a programming point of view a class can be described as a template from which direct instances are generated. In Java a class is a data structure that may contain members.
A member of a class is a class element that defines an attribute or an operation. Each member can be viewed as a sub-object. When a class is declared, an optional member list declares the class members.
An instance of a class is an object based on the class. Creation of an instance from a class is called instantiation.
This article explains how to create a class with one member and how to instantiate it and provides a simple example of an instance being used.
Simply speaking, a polygon can be described as a flat shape with three or more straight sides. The clas program defines a class representing a polygon.
The definition of a polygon states that it has a number of sides, but does not specify how many sides there are. The shapes below are all polygons.
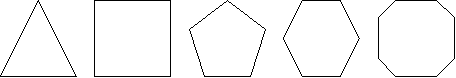
These shapes are actual objects that fall within the more generic category of a polygon. In programming terms, if the polygon is a class, each of these shapes is an instance of the polygon class. To define any of the shapes properly it is necessary to declare how many sides the shape has, and the polygon class thus needs to provide an attribute to allow this declaration to be made. This attribute is provided as a class member.
The clas program declares an instance of the polygon class, called triangle, and specifies the number of its sides as three.
Concepts
|
A class defines the abstract characteristics of a thing (object), including its characteristics and what it can do. From a programming point of view a class can be described as a template from which direct instances are generated. The clas program defines a class identified by polygon to represent a polygon. |
|
|
When a class is defined, the definition includes its members, which describe its characteristics. The members of a class can include data members (constants and variables) and function members (which include methods) which are specific to the class. The definition of the polygon class includes one data member, sides, to specify the number of its sides. |
|
|
An instance of a class is an object that has been created from the class template. A class is only a definition until an instance of the class is created. In object-oriented programming, a class is a template definition of the members in a particular kind of object. Thus, an object is a specific instance of a class; it contains real values instead of variables. The clas program declares an instance of the polygon class, called triangle, and specifies the number of its sides as three. |
|
|
Creation of a new instance from a class template is known as instantiation. Instantiation is performed in the clas program using the new keyword. |
|
|
A definition is a self-contained block of code with a specific purpose. The clas program contains a definition for the polygon class and the clas class, both of which are self-contained blocks of code. |
Source Code
The source code listing is as follows:
|
/* clas.java Class. environment: language Java platform console */ // polygon class polygon { int sides ; } // class containing entry point class clas { public static void main( String[] args ) { polygon triangle ; triangle = new polygon() ; triangle.sides = 3 ; System.out.print( "triangle has " ) ; System.out.print( triangle.sides ) ; System.out.println( " sides." ) ; } } |
|
| Source | |
Compiling and Running
-
Save the source code listing into a file named clas.java. Clicking the Source tab below the listing will open the source code in a new window. The source code may be saved by right-clicking on the Source tab and selecting Save.
-
Launch a Windows command prompt.
-
Navigate to the directory clas.java was saved in.
-
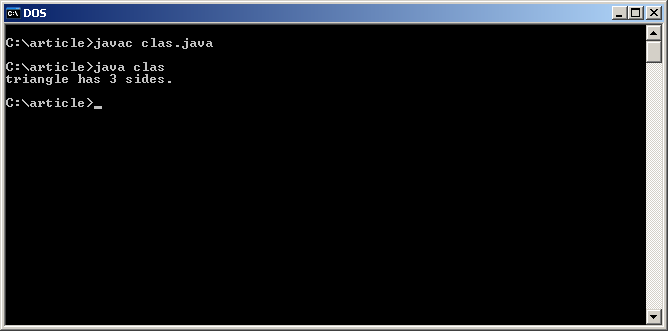
To compile the program type:
> javac clas.java -
To run the program type:
> java clas
Code Explanation
| class polygon { int sides ; } |
A class can be described as a template for objects used by the program. Classes are declared using the class keyword. The format of a simple class definition is as follows:
class identifier { members }
where:
|
class |
is the keyword indicating that a class is being declared. In the definition of the polygon class, as in all class definitions, the keyword is the word class. |
|
identifier |
is the identifier by which it will be possible to refer to the class. The identifier of the class defined here is polygon. |
|
members |
contains the members of the class, which describes its characteristics. The section of the class defined between braces {} consists of member declarations or definitions and is known as the member list. The only member of the polygon class is the sides member which defines how many sides the polygon has. |
The identifier of the class declared above is polygon. The only characteristic of the polygon class is that it contains a sides member.
A member of a class is a class element that defines an attribute or an operation. A class member can exist in a number of forms including a field (or data member) which consists of data contained within the object. The format of a simple field declaration is the same as a simple variable declaration, as follows:
type identifier ;
where:
|
type |
is the type specifier of the field. The type specifier in the declaration of the sides field is int, which specifies a 32-bit integer. |
|
identifier |
is the identifier by which it will be possible to refer to the field. The identifier of the sides field is sides. |
|
; |
closes the declaration and delimits it from the next statement. All statements in Java, including the sides field declaration, are closed with the semicolon character ;. |
|
class clas { ... } |
If a program is executable one of the classes available must have a static main method that serves as the entry point. The main method is a member of the class.
The clas class is included in the clas program to provide the main method, and contains one member - the main method.
|
public static void main( String[] args ) { ... } |
The main method is the entry point and is called when the program starts.
In the clas program, the main method is the only member of the clas class.
Class members may be prefixed by modifiers - a list of keywords that modify the member.
Other than the type specifier, the main method declaration contains two modifiers: public and static.
The private, protected and public modifiers control accessibility to class members. The public modifier declares a member to be visible to everyone. The main method is declared as public because it must be visible to everyone in order to allow the program to be called.
A class member that has been modified with the static keyword is accessible without requiring an instance of the containing class. What this means is that the member can be accessed without declaring any instances based on the class. All that is required is for the member to be declared, as in the example above, and it can be accessed directly. The main method is declared using the static modifier to provide a global mechanism for calling the program, since at the time of calling no instances of the clas class will have been declared.
| polygon triangle ; |
A class constitutes a user-defined type and instances of the class may be represented by variables. When declaring the variable, the class identifier is used as the type.
This statement declares a variable of type polygon named triangle.
| triangle = new polygon() ; |
An instance is an object based on a class. Creation of an instance from a class is called instantiation. Instantiation is the process of creating a specific object which is a member or instance of a class. It involves creating an actual instance of a declared class.
In Java the new keyword is used to instantiate a class.
Expression new polygon() instantiates the polygon class, i.e. it creates an instance of it. The statement above assigns the newly created instance to variable triangle.
A declaration statement and instantiation statement are often combined into one, so the two statements
polygon triangle ;
triangle = new polygon() ;
could be rewritten as
polygon triangle = new polygon() ;
| triangle.sides = 3 ; |
Once a class has been instantiated and the instance has been assigned to a variable, the instance can be accessed via the variable and so can its members.
This statement assigns literal value 3 to the sides member of the triangle variable which represents an instance of the polygon class.
Further Comments
Members of Java classes can be categorised as follows:
|
data member |
constant |
|
|
|
field |
variable of the class |
|
function member * |
method |
implements the computations and actions that can be performed by the class |
|
|
property |
named characteristic associated with reading and writing that characteristic |
|
|
event |
notification that can be generated by the class |
|
|
constructor |
implements actions required to initialise instances of the class |
|
|
destructor |
implements actions to be performed before instances of the class are permanently discarded |
|
nested type |
|
type that is local to the class |
|
* |
Members that can contain executable code are collectively known as the function members of the class. |
This article discusses the field data member. Discussion of other members includes concepts that are outwith the scope of this article.
| home | Home Page |