Borland C++ Compiler: Hello World Program
Introduction
This article explains how to display text in a console program using the Borland C++ Compiler.
The hello program writes “Hello World” to the console.
Concepts
Preprocessor Directives
A preprocessor is a program that converts input data into output that is used as input to another program. In C++ this conversion is performed on source code before the next step of compilation. This phase of translation is called preprocessing. Lines beginning with a # character are directives for the preprocessor.
#include
The most common directive is the #include directive, which copies the full content of a file into the current file. The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to treat the contents of a specified file as if those contents had appeared in the source program at the point where the directive appears.
Files copied with the #include directive usually contain headers for library functions and data types, which must be included before they can be used. For this reason, the #include directive usually appears near the beginning of the source code file. The files included usually contain header code (the components of the code that contain descriptions of its functionality rather than the statements themselves, often referred to as prototypes) and are thus called header files.
The hello program includes <stdio.h>, the C Standard Input and Output Library, to provide the printf function.
Standard Streams
Input and output operations can be performed in C++ using the C Standard Input and Output Library (cstdio, incorporated into a program using the #include <stdio.h> directive). This library uses what are called streams to operate with physical devices such as terminals.
Three standard streams exist: stdin, stdout and stderr, which are automatically created and opened for all programs using the library. The standard streams are channels used by a computer program to communicate with its environment (typically a text terminal) that are connected before the program is executed. The three connections are called standard input, standard output and standard error.
stdio.h is a header that contains declarations of functions used for various standard input and output operations.
The printf function, used in the hello program, outputs characters to the terminal using standard output.
Source Code
The source code listing is as follows:
|
#include <stdio.h> int main() { printf( "Hello World" ) ; return 0 ; } |
|
| Source | |
Compiling and Running
-
Save the source code listing into a file called hello.cpp. Clicking the Source tab below the listing will open the source code in a new window. The source code may be saved by right-clicking on the Source tab and selecting Save.
-
Launch a Windows command prompt.
-
Navigate to the directory hello.cpp was saved in.
-
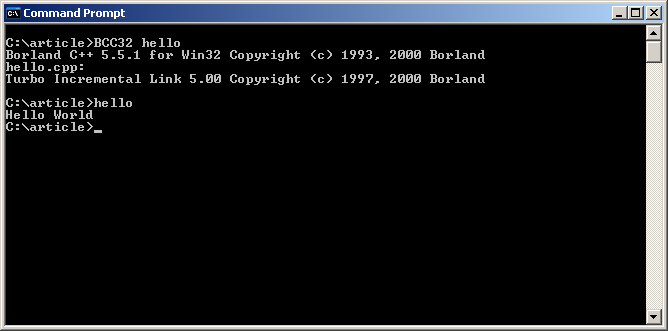
To compile the program, type:
> BCC32 hello -
To test the program, type:
> hello
Code Explanation
| #include <stdio.h> |
The #include directive tells the C++ compiler where to search for definitions. The specified file (stdio.h) is a Standard C library file and is therefore enclosed in angle brackets <>.
stdio.h (which stands for standard input/output) is a header file that declares the functions used to communicate through the standard input and output and is included because it holds the definition of the printf function.
| printf( "Hello World" ) ; |
printf is a function that prints formatted data to the stdout stream.
By default, output is set to the console, where text messages are shown.
The argument passed to the printf function in the statement above is string literal "Hello World", which is printed to the standard output stream by the function. Notice that "Hello World" is enclosed between double quotes " because it is a literal string of characters. Whenever string literals are used, they must be enclosed between double quotes.
Terms
|
A library is a collection of subroutines used to develop software. A library contains a collection of compiled objects consisting of code and data, which are provided to executable programs. Code and data can thus be shared and changed in a modular fashion. The hello program includes <stdio.h>, the C Standard Input and Output Library, to provide the printf function. |
|
|
header file |
Sometimes functions' header and body code are included in a program's code at one location while another copy of the header code is included somewhere else, often in a file containing only header code and thus referred to as a header file, which often has a filename extension of .h. The hello program uses the printf function. The printf function's declaration is contained in header file stdio.h while the header and body that make up the full definition are acquired from the associated library. |
|
A definition is a self-contained block of code with a specific purpose. Definitions are frequently split into header code, which contains information relevant to the user of the code (e.g. a subroutine header contains its name and parameters that are used when the subroutine is called), and body code, or the body, which contains the statements used to execute the code. The hello program includes the stdio.h file which contains the declaration for the printf function. The header and body that make up the full definition are acquired from the associated library. |
|
|
A literal is an expression within source code that represents a constant value. The hello program outputs text represented by literal expression "Hello World". |
| home | Home Page |