The central processing unit (CPU) is the component in a computer that executes program instructions.
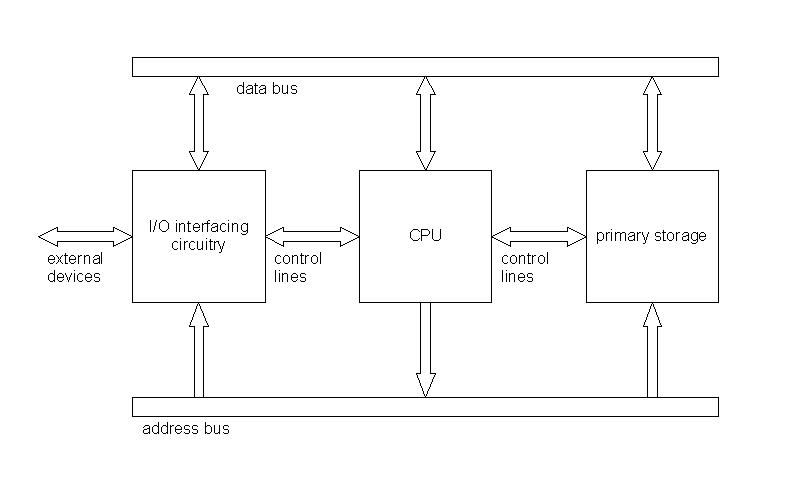
The above diagram illustrates the general hardware architecture of a typical computer, and includes the following components:
|
CPU |
The central processing unit (CPU) executes program instructions. In most applications the CPU controls each bus and one of its functions is to correctly time each bus using control lines so that reliable communication can occur. |
|
primary storage |
Primary storage is memory that the CPU can access (read from or write to) directly. |
|
I/O interfacing circuitry |
The CPU can communicate with the outside world (input/output) via the I/O interfacing circuitry. The I/O interfacing circuitry receives instructions from the CPU via the address bus and data bus and converts these instructions to communicate with external devices. |
|
data bus |
Data retrieved or stored by the CPU is passed along the data bus. |
|
address bus |
The CPU indicates to the other components which data it requires to access by passing a number along the address bus. To access a particular element of primary storage, for instance, the CPU passes the address of that element along the address bus, thus indicating which element is to be accessed. |
The primary work of a computer is performed in the CPU. The CPU is a highly complex extensive set of electronic circuitry that executes stored program instructions.
In order to function, the CPU requires data and that data must be stored where the CPU can access it. Computers use two types of data storage: primary storage and secondary storage. The CPU interacts closely with primary storage, or main memory, referring to it for both instructions and data. Technically, however, memory is not part of the CPU.
Much primary storage is maintained only temporarily, at the time the computer is executing a program. Secondary storage holds permanent or semi-permanent data on an external device, such as a hard disk, a floppy disk, a flash drive or a CD-ROM. In order to access data in secondary storage, the data is temporarily transferred via the I/O interfacing circuitry into primary storage and then accessed by the CPU.
| home | Home Page |